- Home
-
Product
Sectigo
Extended Validation(EV)SSL Organization Validation(OV)SSL Domain Validation(DV)SSL Wildcard SSL Multi-Domain SSL Single-Domain SSL Compare Certificates - About Us
- Contact Us
What Are Electronic Signatures?
Anyone new to this area can be easily confused about what constitutes an electronic signature and how different types of e-signatures compare in terms of evidential power and legality.
At a basic level any mark on an electronic document can be used to capture the signer’s intent to approve or accept the contents of that document. The form of the “mark” or how it was created is not important. What is important is proving who made the mark and that the document was not changed subsequently.
Electronic Signaturesare Categorised As
These signature types and the level of security they provide are explained in more detail below.
-

Click-to-Sign Signatures
-

Advanced Electronic Signatures
-

Basic Electronic Signatures
-

Qualified Signatures
Basic Electronic Signatures

Signatures
These include tick boxes, e-squiggles, scanned images, and typed names. In this category of signature there is no cryptographic protection of the document. So such signatures are not enough to provide strong evidence of who signed or even to protect the document from subsequent change. They can be easily cut/pasted from one document to another. We do not recommend the use of such signatures on their own.

What Are Basic Signatures?
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) and Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) are fully supported in SigningHub. AES and QES provide the highest level of trust and assurance because these use unique signing keys for every signer. This directly links the user’s identity to the signed document such that anyone can verify it on their own using an industry standard PDF reader. Note technically these are also referred to as “digital signatures” rather than “e-signatures”.
-

Present The Document Immediately
-

Capture The Person’s Hand-Signature Mark On The Document
-

Lock The Document From Further Change Using A Server-Side E-Seal
Normally basic e-signatures may or may-not require the user to be registered and their identity validated as a part of this. Regardless of whether or not users are registered with basic e-signatures the signer’s identity is not verifiable directly from the signed document.
Some business applications require users to sign documents immediately without requiring the user to register and have their identity verified with the SigningHub system. Typically use cases include a potential customer visiting a bank, office or shop in person and needing to sign some initial paperwork.
In addition a staff member may also apply their advanced digital signature as a witness for additional security and trust
See What’s Inside A Basic Signature:
After the user has made their e-signature appearance mark on the document, behind the scene SigningHub protects the document by locking it with an advanced e-Seal, using a key that it owns or that belonging to the enterprise account holder (e.g. bank, office, shop etc).
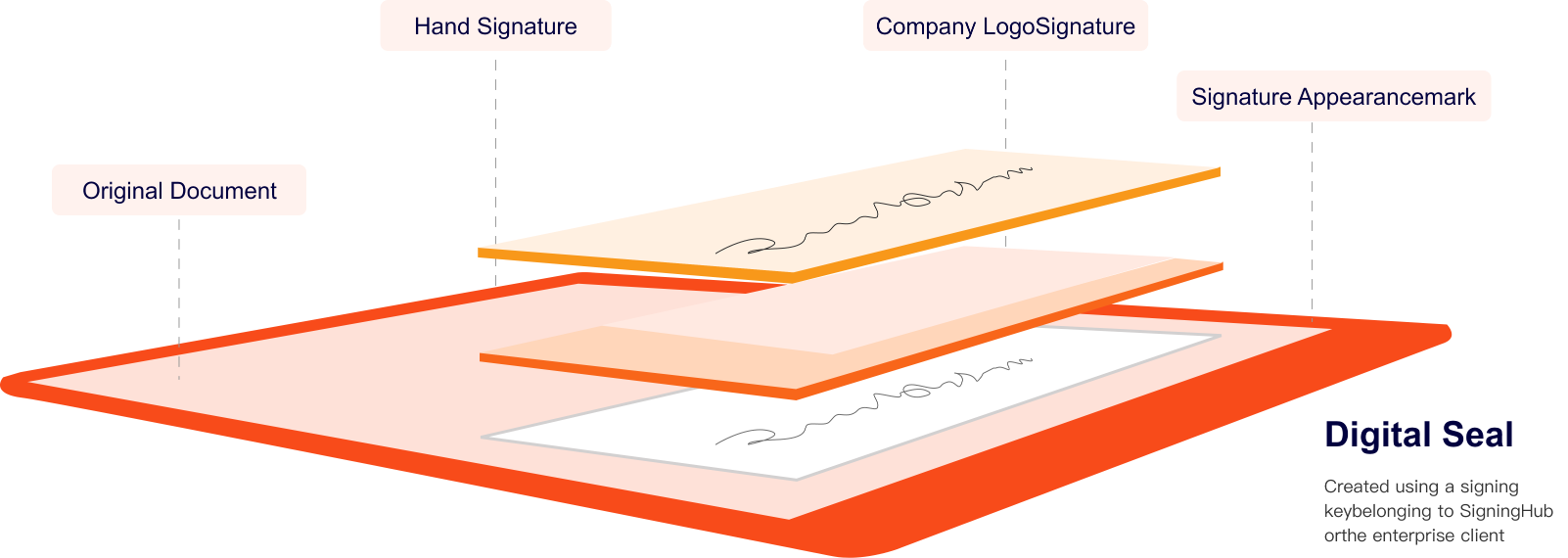
How Basic Signatures Appear When Verified:
Documents signed with a basic e-signature show the person’s signature mark but when verified show that the digital e-seal (technically a digital signature) was applied by the organisation:


Comparing Different Types Of Electronic Signatures
| Click to Sign | Basic e-Signatures | Advanced e-Signatures | Qualified e-Signatures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User Authentication | ||||
| User Consent | ||||
| User’s Signature Mark | ||||
| Document Integrity | ||||
| Bind Signer’s ID to Doc | ||||
| Certify Signature | ||||
| Embedded Evidence | ||||
| Long Term Verifiability |
